Wireless Turbidity Sensors: Enhancing Water Quality Monitoring
- Savio Navaratne
- Nov 6, 2023
- 4 min read

Water quality, once considered a dry topic, has taken a splashy turn towards the exciting as it is of paramount importance in today's world. As environmental consciousness and water conservation efforts continue to grow, the need for reliable monitoring tools has become increasingly crucial. One such tool is the wireless turbidity sensor. This technology provides real-time insights into water quality, making it an invaluable asset for both environmental monitoring and industrial applications. So, grab your snorkel, as we dive into this blog! We'll explore the intricacies of wireless turbidity sensors, including measuring technology, wireless options, the pros and cons, calibration techniques and much more.
Specialists measure water turbidity for several important reasons. Turbidity testing serves as a reliable indicator of overall ecosystem health and helps assess the impact of activities like dredging and construction on water quality. It also indicates pollution levels and ensures compliance with drinking water standards. Particles in water not only affect its appearance but also serve as attachment sites for metals and bacteria, significantly impacting water quality.
Measuring Technology
Turbidity, the cloudiness, or haziness of a fluid caused by large numbers of individual particles, can be an excellent indicator of water quality. Turbidity sensors employ various techniques to measure this parameter accurately:
Nephelometry: This method relies on the scattering of light as it passes through the water sample. A light source emits light into the water, and a detector measures the scattered light at a specific angle. The intensity of scattered light is directly proportional to the turbidity of the water. (Picture a disco in your water sample. A light source sends out rays, and a detector catches the glitzy light scattering off particles. The more sparkle, the higher the turbidity.)
Turbidimetry: Like nephelometry, turbidimetry measures the reduction in light intensity as it passes through the water. The sensor emits light, and a detector measures the transmitted light. The more particles in the water, the less light passes through, indicating higher turbidity.
Laser Scattering: In this method, a laser beam is directed into the water, and detectors measure the scattering patterns of the laser light. This technique provides high precision and is often used in research and industrial applications. (As if a laser beam dances into the water, and sensors watch the funky dance moves of the laser light.)
Wireless Options
Advancements in wireless technology have revolutionised the way we collect data from turbidity sensors. There are several wireless options available to choose from, each with its own set of benefits and limitations:
Wi-Fi: Utilising existing Wi-Fi networks, these sensors can transmit data to a central server or the cloud. This is a cost-effective option if Wi-Fi infrastructure is available and reliable.
Bluetooth: Bluetooth-enabled sensors can send data directly to a nearby device, like a smartphone or tablet. They are suitable for applications that require short-range data collection, they prefer a closer connection, like a romantic dance in the moonlight.
LoRaWAN: LoRa is a low-power, long-range wireless communication technology. It's an excellent choice for remote or outdoor applications where power efficiency is critical.
Cellular Networks: Sensors equipped with cellular connectivity (such as NB-IoT) can send data to a central server from virtually anywhere, making them suitable for remote and mobile monitoring.
The Splashy Pros and Cons
Wireless turbidity sensors offer numerous advantages, but they also come with certain drawbacks:
Pros:
Real-time Monitoring
Wireless sensors provide real-time data, enabling prompt responses to changes in water quality.
Remote Accessibility
With the right connectivity, you can access data from anywhere, enhancing the flexibility of monitoring applications.
Reduced Maintenance
Many wireless sensors are designed for long-term use with minimal maintenance requirements, reducing operational costs.
Data Integration
Wireless sensors can easily integrate with data management systems, allowing for in-depth analysis and historical data storage.
Cons:
Cost
The initial investment for wireless sensors can be higher than traditional monitoring equipment. Like a front-row ticket to a rock concert, but it’s worth the show.
Power Requirements
Depending on the chosen wireless option, some sensors may require a power source, which can be limiting in remote locations.
Data Security
Wireless data transmission requires robust security measures to protect sensitive water quality data from cyber threats.
Calibration of Turbidity Sensors
To fine-tune the dance moves and ensure the accuracy of turbidity measurements, periodic calibration is essential. Here are some steps involved in the calibration process:
Standard Solutions: Calibration standards with known turbidity values are used to calibrate the sensor, quite similar to dance choreography. These standards should cover the expected turbidity range of the application.
Calibration Curve: A calibration curve is created by comparing the sensor's readings to the standard solutions. This curve helps convert the sensor's output into accurate turbidity measurements.
Regular Maintenance: Just like a dancer needs practice, sensors need regular recalibration and maintenance to keep the performance sharp and reliable.
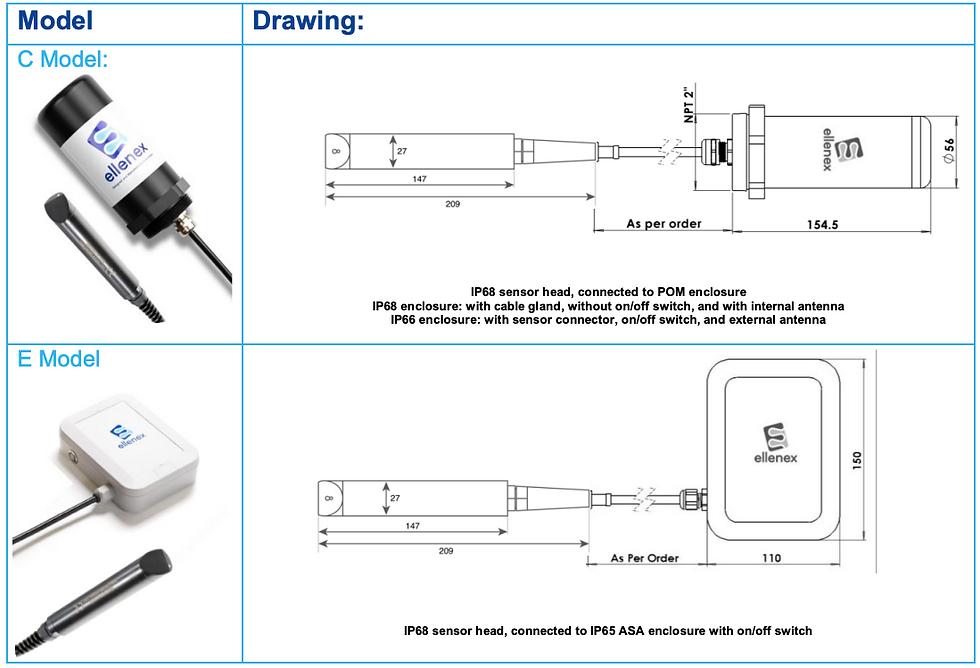
Our Turbidity Sensors
At Ellenex, we take pride in offering state-of-the-art turbidity sensors that utilise cutting-edge ‘Diffusion Infrared (IR) nephelometer technology at a precise 90-degree angle. This ensures unparalleled accuracy in measuring turbidity, giving you crystal-clear insights into your water quality.
What sets up apart? With us, you can choose between two powerful wireless options: LoRaWAN and NB-IoT, tailored to suit your specific needs and operational preferences.
Our sensors are designed to thrive in outdoor applications, enduring the harshest environmental conditions. Durable and built to last, with an ultra-low power consumption, our sensors ensure extended operational lifespans and reduced maintenance overhead.
Moreover, for your convenience our sensors come pre-configured, eliminating the need for post-programming or hardware adjustments. This user-friendly approach ensures that you can get up and running swiftly, focusing on what truly matters – safeguarding water quality and making the most of the data you collect. With our turbidity sensors, you’re not just investing in technology; you’re investing in simplicity, precision, and a future where water quality monitoring is efficient and accessible to all. Additionally, experience seamless device calibration with our latest app - download it now and calibrate on the spot!
Conclusion
Wireless turbidity sensors are invaluable tools for monitoring water quality in diverse applications, from environmental protection to industrial processes. They offer real-time data, remote accessibility, and data integration capabilities. While they come with initial costs and power requirements, their advantages far outweigh the drawbacks. Proper calibration is essential to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the data collected, making these sensors an indispensable part of modern water quality management. As technology continues to advance, wireless turbidity sensors are poised to play an even more significant role in safeguarding our precious water resources.


